One of the most sought-after fabrics in history, silk embodies a symbol of luxury, elegance, and sophistication. Its lustrous sheen and breathability captivates many, which is why it has become the centerpiece of high-end fashion design.
Yet, while the fabric boasts of aesthetically pleasing qualities, it’s important to look beyond the surface. As an eco-fashionista, you may wonder whether the fabric poses risks to the well-being of our planet. Perhaps, you may question its durability before investing in expensive silk garments.
Regardless of your motives, we will disclose key advantages and disadvantages of the silk fabric that every fashion enthusiast should know. So, let’s dive right into it.

The Pros And Cons of Silk Production
Silk is a natural fiber derived from the larvae of domesticated moths. Believe it or not, it takes about 3,000 cocoons to make one yard of silk! This makes it one of the harder textiles to obtain. Its production makes up less than 0.2% of the global fiber market yet constitutes a multi-billion dollar industry.
Like other natural fabrics, silk is a renewable resource, can biodegrade, and uses less water, chemicals, and energy than synthetic fibers.
Generally speaking, we would consider silk a more sustainable fiber than many others. However, its sustainability can vary, based on its production methods since it is an inefficient material to produce. Large quantities of cocoons that inevitably are boiled in water – as a result of that shrunk, silk is hard to be quasi-created and sourced ethically.
With such a quantity of cocoons needed to meet the consumer demand, there are so many leaves and so much land for them to grow on. The processing of the fabric generates high volumes of greenhouse gases, due to the large amounts of manure and fertilizer required to grow mulberry leaves. What’s more, the factories, where cocoons are being processed, require energy to maintain boiling water and steam for production.

The Advantages of Silk
Silk is a material, which like any other, has both its pros and cons. However, the most obvious and outstanding quality of silk lies in its appearance. Obviously, there is no fabric that compares to the classic beauty of silk. It’s easily recognizable and imparts an atmosphere of luxury and sophistication, alongside materials like pearls or gold.
With that said, let’s review the positive qualities of silk, which make it a practical choice for garments of all kinds:
Durability
Besides, one of the remarkable pros of buying silk is its strength, which makes it stand out from both natural and manufactured fabrics. Its fibers are incredibly strong, and when woven together, they resist warping. As a result, silk can be stretched and pulled without showing signs of ripping.
Anti-wrinkling
The impeccable durability of silk ties closely with its anti-wrinkling effect. Compared to other natural materials, silk doesn’t succumb to wrinkling, crushing, and rumpling very easily.
Breathability
When it comes to breathability, silk will be your best companion. The material is hydrophobic, meaning it naturally wicks away moisture from your body, leaving you sweat- and odor-free. This comes in handy especially in hot weather, as the fabric effectively regulates your body temperature, leaving you feeling fresh, airy, and comfortable.

The Disadvantages of Silk
Though, as any material available on the market, silk also has its cons. One of them being durability, or a lack thereof. Silk is likely to show the effects of regular wear-and-tear, much more than other natural fibers. Because of this, the fabric should be reserved for pieces that aren’t used very often. This way, you’ll be able to preserve it for the longest time possible.
Affordability Considerations
A very important aspect for most consumers is the affordability of the piece or material, which they are buying. Ever since the beginning of its production, silk has been an incredibly luxurious fabric, and the price tag reflects that.
If you are looking for cheaper alternatives to mulberry silk, faux silk or silk velvet might be better options. However, purchase them pre-loved, as they’re synthetic fibers made of fossil fuels -the production of which burdens the planet with non-biodegradable textile waste.
Vulnerabilities of The Fabric
Silk is not only more prone to tearing but also elemental damage. Even a bit of water can leave a visible stain that’s impossible to get rid of. What’s more, sunlight weakens the fibers of silk, resulting in tearing and fading. This, however, applies to almost all natural fabrics.
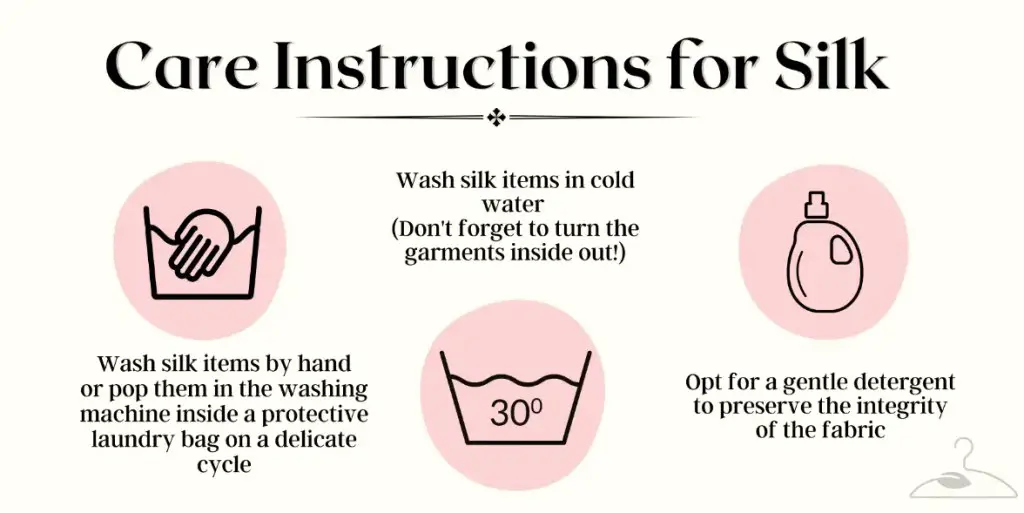
Care Instructions
Considering its vulnerabilities, the only way to preserve the fabric in the long run is to wash it by hand – even if the care label suggests to machine wash it. With a bit of toxin-free detergent, you should wash the fabric in cold water to ensure its longevity. Alternatively, instead of detergent, you can use regular shampoo since just like your hair, silk is made of protein fibers.
Peace Silk As An Alternative
Most silkworms are killed in their cocoons before maturing into a moth, but there is a less cruel alternative to this. An innovative product of silk manufacturing, peace silk or cruelty-free silk, comes from cocoons, from which moths have been allowed to emerge freely. This eliminates the cruelty associated with killing silkworms by baking and steaming them alive.
The Use of Fertilizers
In conventional silk production chemical pesticides and fertilizers are sometimes used, though usually they are not required. Even when they are used in the growing of mulberry trees, they require significantly fewer chemical inputs than cotton and most other natural fibers.
Large Productions of Silk
One mature mulberry tree will produce enough foliage for 100 silkworms. If 3,000 cocoons go into making one yard of fabric, that means there must be at least around 30 trees a year, since mulberry trees lose their leaves annually, at the absolute minimum.
The Energy Behind The Process
Large amounts of energy are used when creating silk, the most energy-intensive part of the process being the procedure of cooking the cocoons. Some analyses have found that silk is 1000 times more efficient in its energy of formation than the process of producing polyethylene.
Creation of Wastewater
It is common for wastewater to be dumped directly into groundwater, which not only contains toxins but also biological waste that can contribute to land degradation. The use of chemicals is relatively low in the process of handling silk, but the use of dyes seems to be relatively high.
The Labor Process Behind Silk
Silk production is labor intensive and tends to take place in countries with low labor costs. Exposure to chemicals through breathing and skin contact during production and material processing can be extremely harmful to workers’ health if proper equipment and safety precautions are not used.

The Real Disadvantages of Silk: The Controversy
Controversy around sustainability extends to make fabrics available on the market, and silk is no exception.
We have already heard about the damage that silk production caused the environment and the way workers in third-world countries are working in sweatshops – a whole other problem, and are being paid fractions of the price we, as consumers, spend on those fabrics. It poses a simple question – is investing in the fabrics really worth it?
Looking Beyond the Lustrous Surface
Sometimes, we should consider the real harm the constant demand for any fabric, not just silk, has on the workers in this industry. Most importantly, we should keep in mind workers whose livelihoods depend on the consumers who continuously indulge in fashion pieces.
Looking at the bigger picture, silk production is not only an issue of workers’ rights but also of plantations, which take up a significant percentage of land worldwide. We also have to consider factories, where most of the globally available clothes are made, which would simply go dry without both the fabrics and the workers.
The sustainability of silk is very debatable as it is not the most, yet not the least sustainable material we know of. The main debate around the fabric revolves around the process, in which hundreds of thousands, if not millions of moths are selectively bred and frozen until breeding season, then crushed and killed in the process of creating silk.
In fact, 3,000 silkworms are killed alive in their cocoons for every 500g of silk produced each year. This amounts to 1.2. trillion silkworms being sacrificed every year to the fabric.
That is one of the many real disadvantages of silk – a not-so-ethical luxury that we indulge in every day.
Issues Around the Global Silk Industry
Human rights violations are nothing new to the fashion industry. However, with silk-producing countries facilitating modern slavery, the global silk industry is among the biggest culprits.
Currently, the biggest exporter of silk is China, alongside other silk-producing countries like India, Uzbekistan, and Thailand. These countries exploit forced and/or child labor, as reported by the Global Slavery Index.
India’s silk industry, in particular, is infamous for trapping underage workers in labor, forcing them to craft silk thread saris (traditional South Asian attire). This has been going on for centuries, with a 1996 Human Rights Watch documenting around 350,000 children workers who produced “silk threads for 12 hours a day, 7 hours a week” under inhumane treatment.
Hence, when considering the advantages and disadvantages of silk, we must think about what our purchases support. Unfortunately, by buying virgin silk from unknown brands, we may be contributing to labor exploitation, inhumane production methods, and cruel working conditions.

Conclusion
The discussion on whether silk production involves animal cruelty is still ongoing, but most people believe it is. While a number of alternatives to silk already exist today, a lot of them are synthetic and derived from fossil fuels. These materials, polyester being the most common, are tied with excessive water use and microplastic shedding, taking up hundreds of years to break down.

